Lesson Note and Plan on Mathematics
Addition of whole numbers
Subject: Mathematics
Theme: Basic operations
Topic: Addition of whole numbers
Date: dd/mm/yyyy
Class: Basic 1
Duration: 35 Minutes
No of Learners: 30
Learning Objectives:
By the end of the lesson learners should be able to:1) add two whole numbers from 1 to 3 with sum less than 5
2 + 1 = 3
2) add two or three whole numbers from 1 to 8 with sum not up to 10
5 + 4 = 9
3) add two or three numbers from 0 to 9 with sum not greater than 18
7 + 9 = 16
4) add 2-digit whole numbers with sum not greater than 40 without exchanging or renaming
14 + 23 = 37
5) cross check numeracy in addition is readable, i.e solve story problems involving addition.
1) two apples plus five apples equals seven apples
2) three extra apples to the seven apples equals ten apples
3) total amount of two apples, one apple and six apples is nine apples
4) one apple, three apples and two apples in all give six apples
5) one apple, three apples and two apples all together give six apples
Rationale:
The lesson will equip the learners with different strategies that they can use to solve real world problems. In our society, learners are always engaging themselves in situations involving quantities. They are always trying to put things together, join them and even break them into pieces while trying to make sense out of it. Exposing them to a variety of word problems involving addition such as buying things with friends and family, etc.Prerequisite/Previous knowledge:
Learners have been taught fraction.Learning Materials:
1. flash cards2. Oranges, apples, paper, balls, Leaves, Bottle tops, Number Beads, etc.
Reference Materials:
1) New Method Mathematics for Primary Schools 1. C. F. Oredugba, R. Ohuche, G. Salahu et al2) Understanding Maths Book 1 African First Pub. Ltd. Marian N. Daud-Osuaght
3) New Approach to Quantitative Reasoning Bk. 1 Rasmed T.A.O. Olayiwola.
Lesson Development:
| STAGE | TEACHER'S ACTIVITY | LEARNER'S ACTIVITY | LEARNING POINTS |
|---|---|---|---|
| INTRODUCTION full class session (3 mins) |
The teacher asks learners: What fractions of the objects drawn below are shaded? 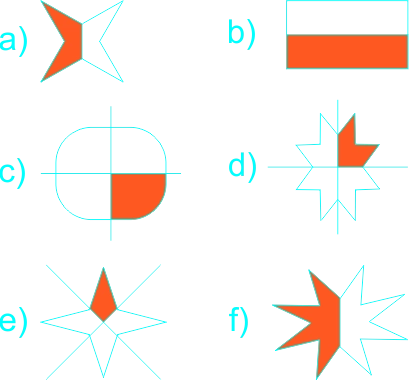
|
Learners expected response: a) Half (½) b) Half(½) c) One-quarter (¼) d) One-quarter (¼) e) One-quarter (¼) f) Half (½) |
Warming up and revising previous lesson on fraction |
| The teacher begins the day's lesson by checking learners' textbook/notebook, thereafter tells a story: 1) There are two apples in a bowl. Peter dropped one more apple inside the bowl. How many apples are there altogether? The teacher tells learners that, we can also read this as two apples plus one apple equal three apples 2) There are 3 sweets in the first jar and there is 1 sweet in the second jar. How many sweets are there altogether? |
Learners expected respond: 1) two apples and one apple equal three apples. 2) 3 sweets and 1 sweet equal 4 sweets. |
Developing the idea of the concept Addition. | |
| DEVELOPMENT Step 1. Group Work (5 mins) |
The teacher guides the learners to form four groups and asks them to choose their leaders and secretaries. | Learners choose their group leaders and secretaries. | Inculcating leadership skills, competitive spirit, cooperation, teamwork and a sense of responsibility among learners. |
| The teacher introduce the concept using countable manipulatives (physical objects) The teacher asks learners to count: a) the numbers of persons they have in there group b) the numbers of fingers in your left and right hands and add them together. |
Learners added corectly the countable manipulatives (physical objects) a) four persons in a group. b) five fingers on the left hand, five fingers on the right hand added together gives ten fingers. |
Through practical demonstrations using concrete objects and shapes, guide the pupils to discover the concept of addition. | |
| ACTIVITY 1 Step 2. Group Work (3 mins) Add two whole numbers from 1 to 3 with sum less than 5 |
The teacher uses other countable manipulatives (physical objects) 1) 2) 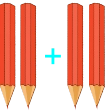
|
Learners added corectly the countable manipulatives (physical objects) 1) 2) 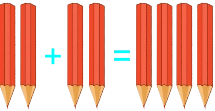
| |
| ACTIVITY 2 Step 3. Group Work (3 mins) Add two or three whole numbers from 1 to 8 with sum not up to 10 |
The teacher uses other countable manipulatives (physical objects) 1) 
2) 
The teacher tells learners that when you add zero to any number the sum is the number. Learners draw and count on there notebooks. 1) 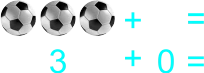
2) 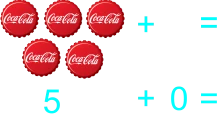
3) 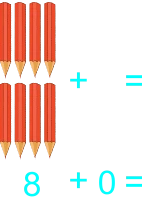
4) 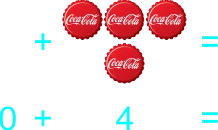
5) 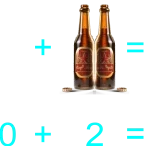
|
Learners added corectly the countable manipulatives (physical objects) 1) 
2) 
Learners expected answer 1) 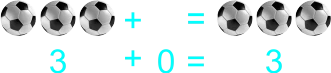
2) 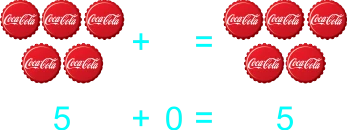
3) 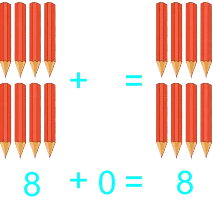
4) 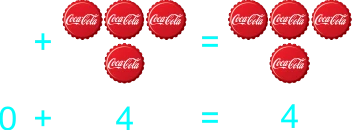
5) 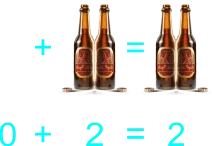
|
|
| ACTIVITY 3 Step 4. Group Work (3 mins) Add two numbers from 0 to 9 with sum not greater than 18 |
The teacher starts transferring addition to paper by using illustrated sums/plus. Also having students draw objects they can count. 1) 2 balls and 5 ball 2) 2 balls plus 5 ball 3) 2 balls + 5 ball 4) 2 + 5 5) 5 pencils and 0 pencils 6) 5 pencils plus 0 pencils 7) 5 pencils + 0 pencils 8) 5 + 0 9) 8 botton caps and 5 botton cap 10) 8 botton caps plus 5 botton cap 11) 8 botton caps + 5 botton cap 12) 8 + 5 13) 9 drinks and 8 drink 14) 9 drinks plus 8 drink 15) 9 drinks + 8 drink 16) 9 + 8 |
Learners expected result 1) 2 balls and 5 ball equals 7 balls 2) 2 balls plus 5 ball equals 7 balls 3) 2 balls + 5 ball = 7 balls 4) 2 + 5 = 7 5) 5 pencils and 0 pencils equals 5 pencils 6) 5 pencils plus 0 pencils equals 5 pencils 7) 5 pencils + 0 pencils = 5 pencils 8) 5 + 0 = 5 9) 8 bottle caps and 5 bottle caps equals 13 bottle caps 10) 8 bottle caps plus 5 bottle caps equals 13 bottle caps 11) 8 bottle caps + 5 bottle caps = 13 bottle caps 12) 8 + 5 = 13 13) 9 balls and 8 ball equals 17 balls 14) 9 balls plus 8 ball equals 17 balls 15) 9 balls + 8 ball = 17 balls 16) 9 + 8 = 17 |
|
| ACTIVITY 4 STEP 5 3 mins. Addition of 3 whole numbers with sum less than 18 |
The teacher guides the learners to use a number line in counting on.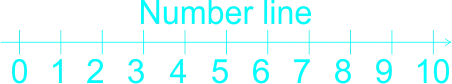
If the sum is 2 + 3, for example, learners can put their finger on the two to start with, and then count up three places to reach 5. They no longer need to count out the 2 first to reach the solution. Etc. 1) 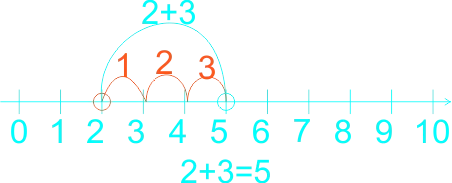
2) 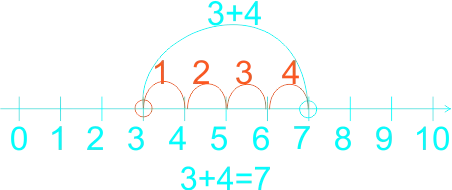
3) 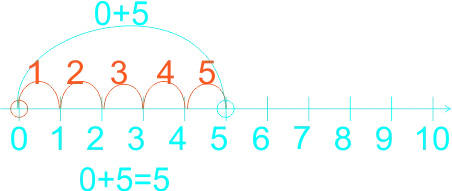
|
Learners listen to teacher. | Learners adding by counting out every number in a sum to reach the total solution. |
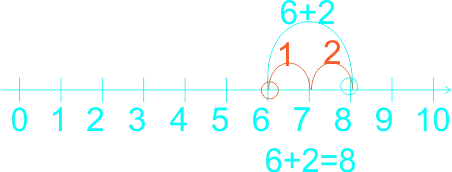
The teacher guides learners to sum the following using the number line
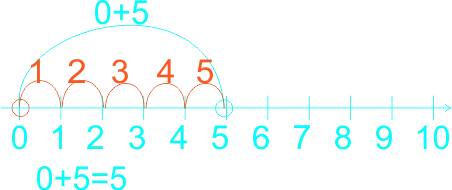
1) 2 + 5 = ------ 2) 0 + 3 = ------ 3) 6 + 3 = ------ 4) 0 + 5 = ------ 5) 1 + 5 = ------ 6) 1 + 2 = ------ 7) 6 + 2 = ------ |
Learners expected answers: 1) 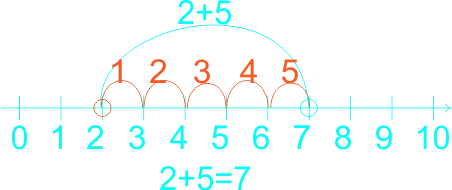
2) 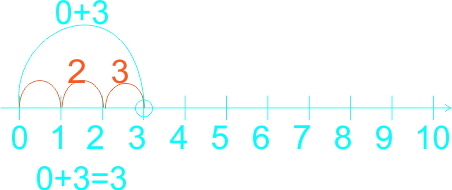
3) 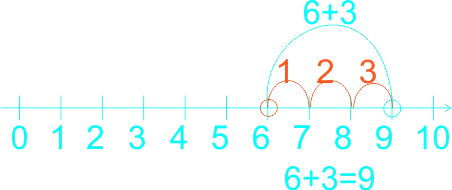
4) 
5) 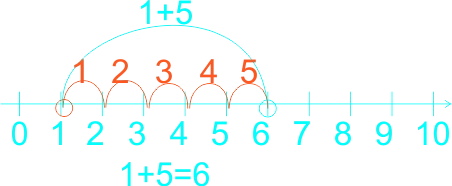
6) 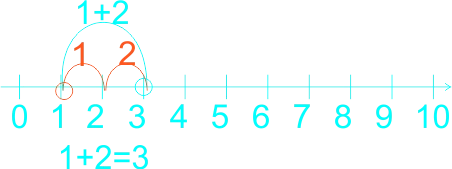
7) 
|
||
| ACTIVITY 5 STEP 6 5 mins. Counting Up |
The teacher guides the pupils to use the same “counting up” strategy in their heads to carryout horizontal addition. Example 4 + 3 i) Learners start with a closed first and say “4”. ii) Learners then count up “5, 6, 7”, extending three fingers one at a time. iii) Learners now have three fingers extended (i.e three steps). They started with a 4 in their first and then counted up 3 steps, so the answer is 7. The teacher guides learners to sum the following numbers. 1) 1 + 1 = [ ] 2) 0 + 2 = [ ] 3) 5 + 0 = [ ] 4) 1 + 3 = [ ] For three digits whole numbers, add the first two digits or the last two digits, then add the results as two digits numbers 5) 5 + 0 + 9 = [ ] 6) 7 + 4 + 3 = [ ] 7) 8 + 4 + 5 = [ ] 8) 6 + 5 + 4 = [ ] 9) 6 + 4 + 5 = [ ] 10) 3 + 5 + 7 = [ ] |
Learners sum the numbers correctly 1) 1 + 1 = [2] 2) 0 + 2 = [2] 3) 5 + 0 = [5] 4) 1 + 3 = [4] 5) 5 + 0 + 9 = 5 + 9 = [14] 6) 7 + 4 + 3 = 11 + 3 or 7 + 7 = [14] 7) 8 + 4 + 5 = 12 + 5 or 8 + 9 = [17] 8) 6 + 5 + 4 = 11 + 4 or 6 + 9 = [15] 9) 6 + 4 + 8 = 10 + 8 or 6 + 12 = [18] 10) 3 + 5 + 7 = 8 + 7 or 3 + 12 = [15] |
Addition of two or three numbers from 0 to 9 with sum not greater than 18 |
| The teacher guides the pupils to use the same “counting up” strategy in their heads to carryout vertical/column addition 1) 3 + 5 _____ _____ 2) 9 + 0 _____ _____ 3) 3 + 3 _____ _____ 4) 7 + 2 _____ _____ 5) 4 + 4 _____ _____ 6) 1 + 4 _____ _____ 7) 3 + 2 _____ _____ 8) 2 + 5 _____ _____ 9) 8 + 1 _____ 9 _____ Finding the ten The teacher introduces the learners to a mental mathematics trick that will help learners develop their procedural fluency. Instead of adding two numbers together as they are, the learners are encourage to add them up to 10, and then add the remainder to that 10. For example, the process for 7 + 5 is: To turn 7 into 10, we need 3 (7 + 3 = 10) To turn that 3 into 5, we need 2 (3 + 2 = 5) therefore. 10 + 2 = 12 is equivalent to 7 + 5 = 12 NOTE: This method is used only when the numbers can be added up to ten The teacher guides the learners to use mental mathematics to sum the following whole numbers 1) 9 + 8 = ----- 2) 7 + 6 = ----- 3) 4 + 7 = ----- |
Learners listen to teacher and sum the following 1) 3 (3 and IIIII steps) + 5 _____ 8 _____ 2) 9 (9 and no step) + 0 _____ 9 _____ 3) 3 (3 and III steps) + 3 _____ 6 _____ 4) 7 (7 and II steps) + 2 _____ 9 _____ 5) 4 (4 and IIII steps) + 4 _____ 8 _____ 6) 1 (1 and IIII steps) + 4 _____ 5 _____ 7) 3 (3 and II steps) + 2 _____ 5 _____ 8) 2 (2 and IIIII steps) + 5 _____ 7 _____ 9) 8 (8 and I step) + 1 _____ 9 _____ Learners use mental mathematics trick to sum the following whole numbers 1) 9 + 8 = (9 + 1 = 10) (1 + 7 = 8) :. 9 + 8 = 10 + 7 = 17 2) 7 + 6 = (7 + 3 = 10) (3 + 3 = 6) :. 7 + 6 = 10 + 3 = 13 3) 4 + 7 = (4 + 6 = 10) (6 + 1 = 7) :. 4 + 7 = 10 + 1 = 11 |
||
| ACTIVITY 6 STEP 7 3 mins. (Add 2-digit whole numbers with sum not greater than 40 without exchanging or renaming) |
The teacher guides learners to add 2-digit whole numbers with sum not greater than 40 using horizontal methed | Learners add 2-digit whole numbers with sum not
greater than 40 using horizontal methed 1) 14 + 23 = 10 + 4 + 20 + 3 = 10 + 20 + 4 + 3 = 30 + 7 = 37 2) 21 + 17 = 20 + 1 + 10 + 7 = 20 + 10 + 1 + 7 = 30 + 8 = 38 |
Addition of 2-digit whole numbers with sum not greater than 40 |
| The teacher guides learners to add 2-digit whole numbers with sum not greater than 40 using vertical/column method The teacher guides pupils to arrange the numbers under tens and units, then add the units and add the tens. |
Learners arrange the numbers under tens and units, then add the units and add the tens. 1) 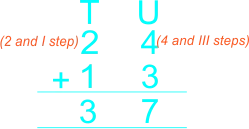
2) 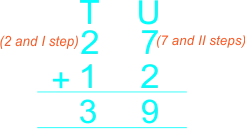
3) 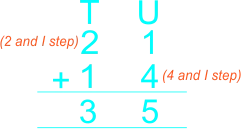
4) 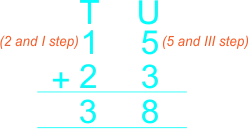
|
||
| STEP 8 3 mins. Word problems |
The teacher tells learners how they can identify addition in word problems even when they aren’t clearly specified. The teacher started by introducing them to the language of addition, such as: X plus y, X extra, X added to, total amount, in all, altogether etc. The teacher guides learners to solve word problems. |
Learners solve word problem correctly 1) John has 2 pencils and Janet has 6 pencils. How many pencils do they have altogether? Solution John has 2 pencils Janet has 6 pencils Altogether they have 8 pencils 2) Fade has 5 goats and Afolabi has 4 goats. How many goats do they have altogether? Solution Fade has 5 goats Afolabi has 4 goats Altogether they have 9 goats |
Real-life activities involving subtraction |
| Evaluation Full class session (5 mins) |
Ask the following questions to evaluate the achievement of the set objectives. Copy and complete the following using the vertical/column method. 
5) Mother gave Jude 3 beads and Susan 4 beads. How many beads do they have altogether? |
Learners expected response: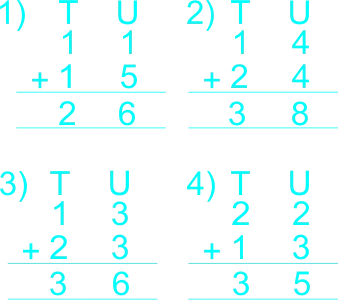
5) Jude has 3 beads Susan has 4 beads Altogether they have 7 beads |
Confirming the achievement of the set objectives. |
|
|
|||
| Conclusion, full class session (3 mins) Learners can add numbers – horizontally – vertically – on the number line. |
The teacher asks learners: 1) Use horizontal method to find the sum of 13 + 26 2) Use vertical method to find the sum of 11 + 23 3) Use the number line to complete the addition 3 + 4 |
Learners expected answers: 1) 13 + 26 = 10 + 3 + 20 + 6 = 10 + 20 + 3 + 6 = 30 + 9 = 39 2) 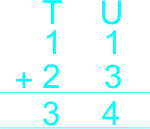
3) 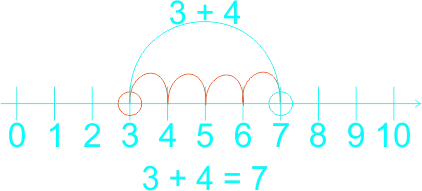
|
Communication: This is developed through answering questions verbally and interpreting the silent signs of teammates during the activities. |
| ASSIGNMENT | The teacher gives learners a take home Copy and complete the following using the vertical/column method. 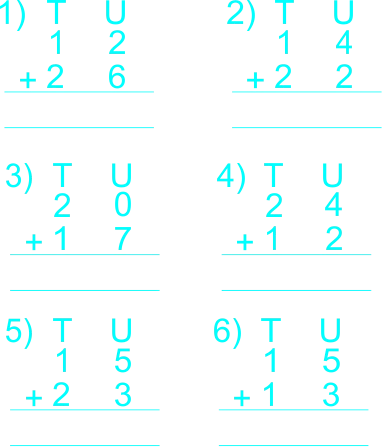
Add the following using horizontal method 1) 2 1 + 1 8 2) 14 + 22 3) 24 + 14 4) 16 + 21 5) 12 + 26 6) 15 + 23 Word problems 1) Mary has 7 bottles and Peter has 1 bottle. How many bottles do they have in all? 2) Ayo has 20 apples and Bili has 14 apples. How many apples do they have altogether? 3) Mufi and Ego were given 4 books each. How many books do they have altogether? 4) I have three eggs and my sister has 4. How many eggs are there altogether? 5) Dele sold 5 cups and Ayo sold 4 cups. How many cups were sold in all? 7) Mufi has 21 beads and Jude has 15 beads. How many beads do they in total? 8) Dele has 23 cups and Ayo has 16 cups. How many cups do they have altogether? |
Learners answer other questions. | Improving their level of understanding on addition. |