Lesson Note and Plan on Mathematics
Subtraction of whole numbers
Subject: Mathematics
Theme: Basic operations
Topic: Subtraction of whole numbers
Date: dd/mm/yyyy
Class: Basic 1
Duration: 35 Minutes
No of Learners: 30
Learning Objectives:
By the end of the lesson learners should be able to:1) subtract from whole numbers not greater than 9
6 – 2 = 4
2) subtract from whole numbers not greater than 18
12 – 5 = 7
3) subtract from whole numbers not greater than 40
36 – 23 = 13
4) Use vertical/column in subtraction of whole numbers not greate than 40
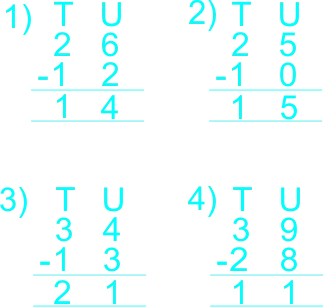
5) solve story problems involving subtraction of whole numbers.
From 16 eggs, there are 9 broken eggs. There are 7 eggs left.
Rationale:
Subtraction is apart of our everyday lives and therefore an important concept to develop early. We need to understand how to subtract in order to engage with society effectively as we use subtraction when dealing with money, cooking, travel and time, among countless other daily experiences.Prerequisite/Previous knowledge:
Learners have been taught addition of whole numbers.Learners have a sound understanding of place value. They understand that in a two-digit number, the left-hand digit represents lots of ten, and the right-hand digit represents ones.
Learning Materials:
1. flash cards2. countable manipulatives (tokens, bottle caps, cut-out pieces of card, anything small)
3. paper and a crayon
4. Jar/basket/bowl etc
5. sweets, apple etc.
Reference Materials:
1) New Method Mathematics for Primary Schools 1. C. F. Oredugba, R. Ohuche, G. Salahu et al2) Understanding Maths Book 1 African First Pub. Ltd. Marian N. Daud-Osuaght
3) New Approach to Quantitative Reasoning Bk. 1 Rasmed T.A.O. Olayiwola.
Lesson Development:
| STAGE | TEACHER'S ACTIVITY | LEARNER'S ACTIVITY | LEARNING POINTS |
|---|---|---|---|
| INTRODUCTION full class session (3 mins) |
The teacher asks learners: What is the sum of 11 and 23? |
Learners expected response: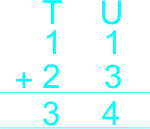 |
Warming up and revising previous lesson on addition |
| The teacher begins the day's lesson by checking learners' textbook/notebook, thereafter tells a story: 1) There are 5 mangoes in a bowl. Ahmed took 2 mangoes out. How many mangoes remain in the jar? The teacher tells learners that, we can also read this as 5 mangoes take away 2. 2) There are 4 Oranges in a bowl. Chika gave no Orange to Bisola. How many Oranges remain in the bowl? The teacher tells learners that, we can read it as ‘4 take away 0’. 3) There are 3 Mangos in a bowl. Chika gave 3 Mangos to Bisola. How many Oranges remain in the bowl? The teacher tells learners that, we can read it as ‘3 take away 3’. |
 Learners expected respond: 1) 5 Mangoes take away 2 leaves 3. 2) 4 Oranges take away 0 leaves 4. 3) 3 Mangoes take away 3 leaves 0. |
Developing the idea of the concept Subtraction. | |
| DEVELOPMENT Step 1. Group Work (5 mins) |
The teacher guides the learners to form four groups and asks them to choose their leaders and secretaries. | Learners choose their group leaders and secretaries. | Inculcating leadership skills, competitive spirit, cooperation, teamwork and a sense of responsibility among learners. |
| The teacher introduce the concept using countable manipulatives (physical objects) The teacher uses a little bit of prompting to guide the learners to answer correctly: 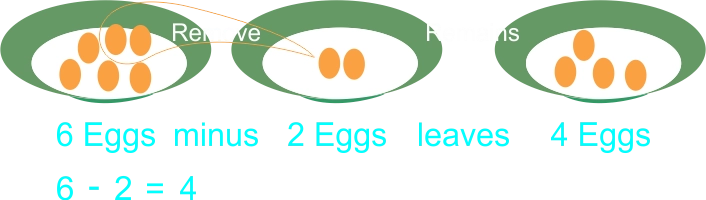 |
Learners subtracted corectly the countable manipulatives (physical objects)
1) 6 take away 2 leaves 4. 6 minus 2 leaves 4. 6 – 2 = 4 2) 7 take away 5 leaves 2. 7 minus 5 leaves 2. 7 – 5 = 2 |
Through practical demonstrations using concrete objects and shapes, guide the pupils to discover the concept of addition. | |
| ACTIVITY 1 Step 2. Group Work (3 mins) Subtraction of whole numbers not greater than 9 |
The teacher uses other countable manipulatives (physical objects) to guides learners to subtract whole numbers correctly. The teacher uses other countable manipulatives (physical objects) Copy and complete the following. a) 7 take away 4 leaves 7 minus 4 leaves 7 – 4 = _____ b) 6 take away 1 leaves 6 minus 1 leaves 6 – 1 = _____ c) 8 take away 6 leaves 8 minus 6 leaves 8 – 6 = _____ d) 9 take away 3 leaves 9 minus 3 leaves 9 – 3 = _____ e) 4 take away 1 leaves 4 minus 1 leaves 4 – 1 = _____ The teacher tells learners that when you subtract zero from any number the answer is the number. Learners draw and count on there notebooks. 1)  2)  |
Learners subtract corectly the countable manipulatives (physical objects)
1)  2)  3)  4)  a) 7 take away 4 leaves 3 7 minus 4 leaves 3 7 – 4 = 3 b) 6 take away 1 leaves 5 6 minus 1 leaves 5 6 – 1 = 5 c) 8 take away 6 leaves 2 8 minus 6 leaves 2 8 – 6 = 2 d) 9 take away 3 leaves 6 9 minus 3 leaves 6 9 – 3 = 6 e) 4 take away 1 leaves 3 4 minus 1 leaves 3 4 – 1 = 3 | |
| ACTIVITY 2 Step 3. Group Work (3 mins) Subtract, using column method. |
The teacher starts transferring subtraction to paper by using column method. The teacher guides the learner to use matches to do the subtraction of numbers from the given number. The teacher guides the pupils to discover the concept of subtraction using story problem. Lead them to realise that ‘take away’ and ‘minus’ are the same as subtract. Lead them to use the minus (–) symbol. | Learners expected result 1) 8 (IIIIIIII remove IIIII) - 5 _____ 3 _____ 2) 4 (IIII remove I) - 1 _____ 3 _____ 3) 5 (IIIII remove II) - 2 _____ 3 _____ 4) 9 (IIIIIIIII remove IIIIIII) - 7 _____ 2 _____ 5) 3 (III remove III) - 3 _____ 0 _____ 6) 7 (IIIIIII remove IIIII) - 5 _____ 2 _____ |
Learners subtracted correctly whole numbers not greater than 9 |
| ACTIVITY 3 STEP 4 3 mins. Using number line |
The teacher guides the learners on how to use a number line in subtraction.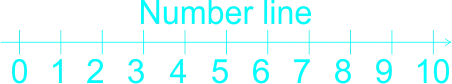 The teacher reminded the learners on the use of the number line in addition, that in addition we do counting on that is, counting forward, for example If the sum is 2 + 3, for example, learners put their finger on the two to start with, and then count up (forward) three places to reach 5. They no longer need to count out the 2 first to reach the solution. Etc. 1) 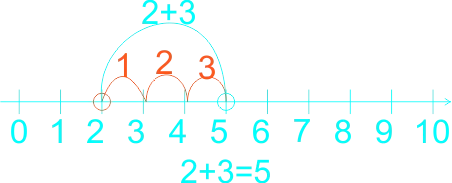 2) 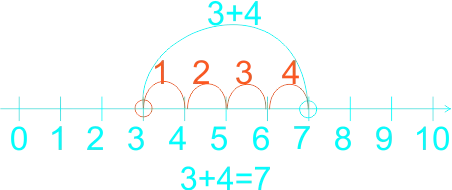 3) 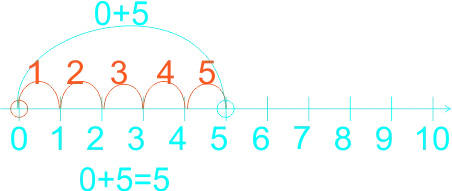 In subtraction, Using number line we count backward 1) 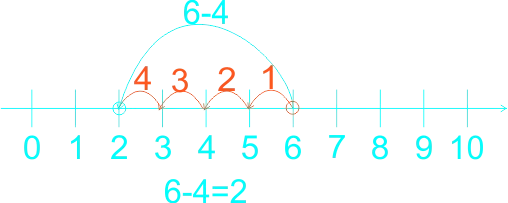 2) 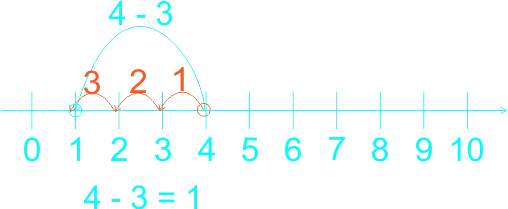 3) 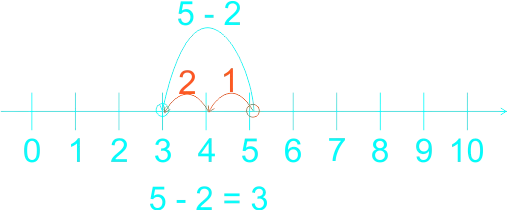 |
Learners listen to teacher. | Use number line in subtraction of whole numbers |
The teacher guides the pupils to subtract whole numbers by counting backwards practically using fingers. Let them do the counting by heart. The teacher guides the weak pupils to use counters, thereafter, use the number line. 1) 5 - 4 = ------ 2) 4 - 4 = ------ 3) 7 - 3 = ------ 4) 8 - 3 = ------ 5) 9 - 4 = ------ 6) 9 - 7 = ------ |
Learners expected answers: 1) 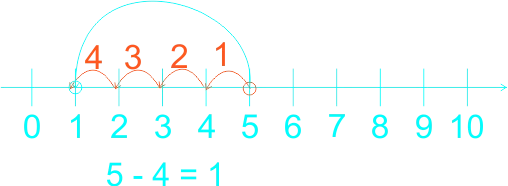 2) 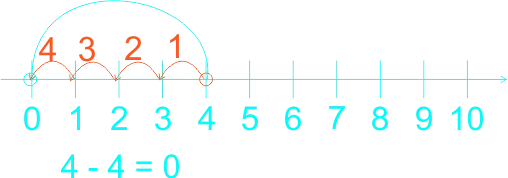 3) 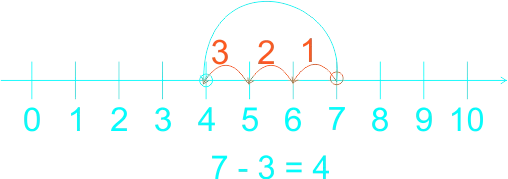 4) 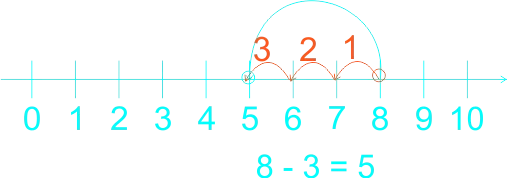 5) 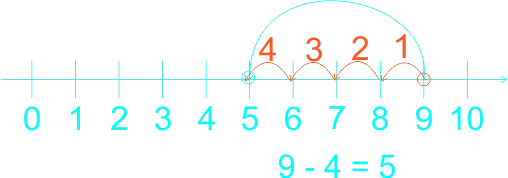 6) 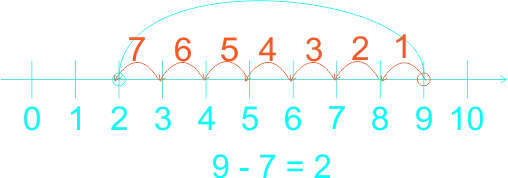 |
Learners subtracting by counting out every number to the left to reach the total solution. | |
| ACTIVITY 4 STEP 5 5 mins. Subtraction of whole numbers not greater than 18 |
The teacher introduces the learners to a mental mathematics trick that will help learners develop their procedural fluency. Instead of counting the upper number and removing the lower number from the upper number to get the result, the learners are encourage to use their fingers to add a number to the lower number that makes it equal to the upper number. For example, the process for 7 - 5 is: extending two fingers one at a time, the first finger will be 6, next 7, i.e we counted 2 fingers to get to 7 Hence to make 5 equal to 7, we need 2 2 is the result of subtracting 5 from 7) 7 - 5 = 2 The teacher guides the learners to use mental mathematics to subtract the following whole numbers 1) 4 - 1 = ----- 2) 5 - 2 = ----- 3) 7 - 3 = ----- 4) 9 - 3 = ----- 5) 5 - 5 = ----- |
Learners listen to teacher and sum the following 1) 4 - 1 (2, 3, 4. i.e 3 steps to get to 4) 4 - 1 = 3 2) 5 - 2 (3, 4, 5. i.e 3 steps to get to 5) 5 - 2 = 3 3) 7 - 3 (4, 5, 6, 7. i.e 4 steps to get to 7) 7 - 3 = 4 4) 9 - 3 (4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9. i.e 6 steps to get to 9) 9 - 3 = 6 5) 5 - 5 (0. i.e no step needed to get to 5) 5 -5 = 0 |
Subtraction of whole number through mental mathematics trick |
| The teacher guides learners on subtraction of whole numbers not greater than 18. Use horizontal subtraction. | Learners subtracted whole numbers not greater than 18 using mental mathematics. a) 11 – 7 (8, 9, 10, 11 i.e 4 steps counted to get to 11) 11 - 7 = 4 b) 13 – 6 (7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13. i.e 7 steps counted to get to 5) 13 - 6 = 7 c) 15 – 5 (6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15. i.e 10 steps counted to get to 15) 15 - 5 10 d) 16 – 10 (11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16. i.e 6 steps counted to get to 16) 16 - 10 = 6 e) 17 – 11 (12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17. i.e 6 steps counted to get to 17) 12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17 17 - 11 = 6 f) 12 – 8 (9, 10, 11, 12. i.e 4 steps counted to get to 12) 12 - 8 = 4 g) 14 – 6 (7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14. i.e 8 steps counted to get to 14) 14 - 6 = 8 | ||
The teacher remainded the learners arrangement of digits under tens and units, and gudes learners to use vertical(column) to subtract whole numbers not greater than 18.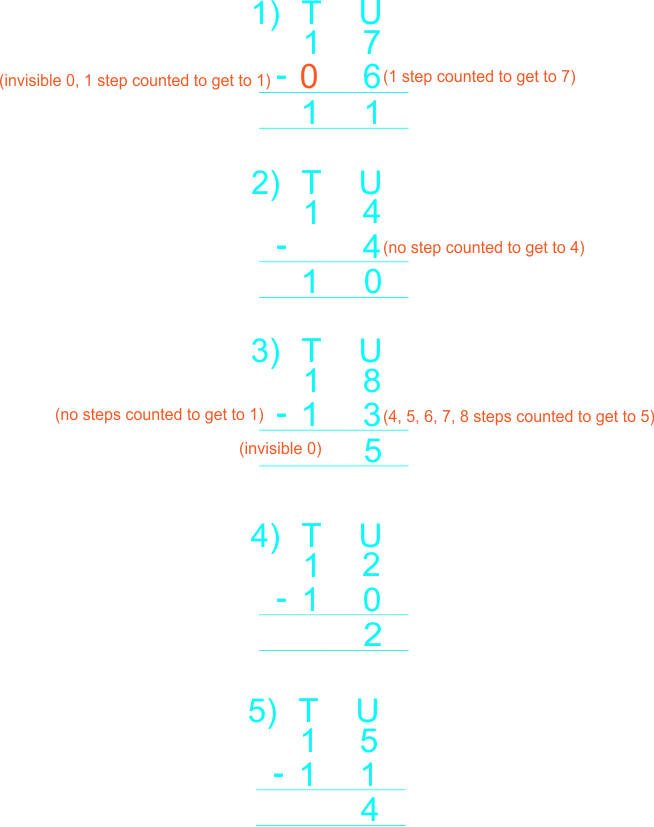 The teacher guides learners to subtracts the following whole numbers. 1) 16 – 5 2) 18 – 8 3) 15 – 13 4) 18 – 12 |
Learners listen to teacher and subtracts the following whole numbers 1) 16 – 5 2) 18 – 8 3) 15 – 13 4) 18 – 12 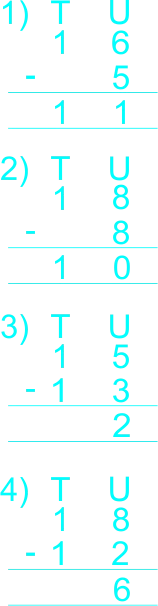 |
||
|
|
|||
| ACTIVITY 5 STEP 6 5 mins. Subtraction of whole numbers not greater than 40 |
The teacher demonstrates to learners on the board how to subtract whole numbers no greater than 40.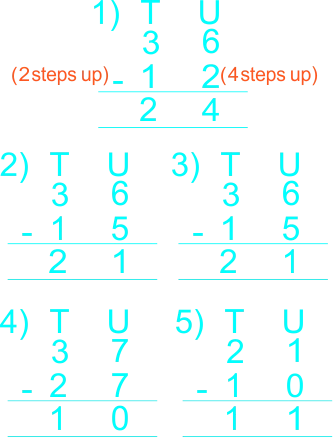 The teacher guide the pupils to arrange 2-digit numbers in vertical columns. Let them realise that when they carry out vertical/column subtraction, they need to start from the units column. |
Learners follow teacher's example to do the following 1) 30 – 10 2) 29 - 13 3) 38 - 21 3) 34 - 21 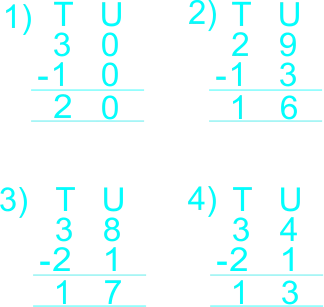 |
vertical/column subtraction of whole numbers not greater than 40 |
| STEP 6 3 mins. Word problems |
The teacher tells learners how they can identify subtraction in word problems even when they aren’t clearly specified. The teacher started by introducing them to the language of subtraction, such as: X from y, X take-away, X minus, etc. The teacher guides learners to solve word problems. |
Learners solve word problem correctly 1) From 16 eggs, there are 9 broken eggs. How many eggs are left? Solution 16 - 9 = 7 There are 7 eggs left. Altogether they have 8 pencils 2) From 21 tea mugs, 11 tea mugs are taken. How many tea mugs are left? Solution 21 - 11 = 10 There are 10 tea mugs left. |
Real-life activities involving subtraction |
| Evaluation Full class session (5 mins) |
Ask the following questions to evaluate the achievement of the set objectives. Use vertical method to work out the following 1) 30 - 10 2) 29 - 13 3) 38 - 21 4) 34 - 21 5) There are 16 cupcakes. 11 cupcakes are eaten. How many cupcakes are left? |
Learners expected response: 5) There are 5 cupcakes left |
Confirming the achievement of the set objectives. |
| Conclusion, full class session (3 mins) | Learners have learnt that Subtraction means ‘take-away’ or minus. 1) The symbol used for minus is –. 2) Numbers can be subtracted from each other by counting backwards using number line. 3) Numbers can be subtracted from each other by using concrete objects. 4) Numbers can be subtracted by using horizontal and vertical methods. The teacher asks learners: Use horizontal, vertical and number line to subtract 10 from 12 |
Learners expected answers: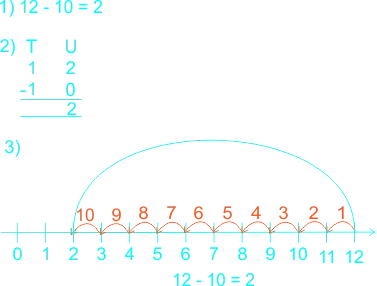 |
Communication: This is developed through answering questions verbally and interpreting the silent signs of teammates during the activities. |
| ASSIGNMENT | The teacher gives learners a take home Subtract the following using horizontal and vertical method 1) 35 - 14 2) 26 - 23 3) 25 - 11 4) 16 - 10 Word problems 1) There are 32 oranges, 21 oranges are taken. There are ____ oranges left. 2) There are 28 teaspoons, 15 teaspoons are broken. How many teaspoons are left? 3) There are 22 bowls, 9 bowls are broken. how many bowls are left? |
Learners answer other questions. Copy and complete the following using the vertical/column method. 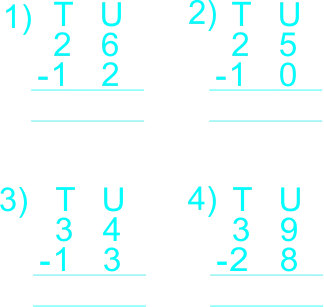 |
Improving their level of understanding on subtraction. |