ASEI Lesson Plan Format
Lesson Note on Chemistry
Theme: Acids Bases & Indicators
Topic: Acids Bases & Indicators II
Sub Topic: Reactivity Series of Metals using Dilute HCl
Date: dd/mm/yyyy
Class: S.S.S 2
Duration: 35 Minutes
No of Learners: 30
Learning Objectives:
By the end of the lesson learners should be able to:Arrange the metals A, B, and C in order of their reactivity after reacting with dilute HCl
Define a reactivity series.
- the more vigorous its reactions are
- the more easily it loses electrons in reactions to form positive ions (cations)
Metal A reaction with dilute acids was rapid, bubbles and hissing sounds are produced, the test tube becomes warm and a colourless solution was formed. Metal A is probably Magnesium.
Mg(s) + 2HCl(aq) → MgCl2(aq) + H2(g)↑Metal B reaction with dilute acids was more rapid than metal A, bubbles are produced, the test tube was hot/warm than that of metal A and a colourless solution was form. Metal B is probably Calcium.
Ca(s) + 2HCl(aq) → CaCl2(aq) + H2(g)↑Metal C reaction with dilute acids was much less vigorous i.e very slow, with much smaller bubbles produced and pale green solutions formed when reaction went to completion, a yellow showery sparks and black solid were produced when the heat was applied. Metal C is probably Iron.
Fe(s) + 2HCl(aq) → FeCl2(aq) + H2(g)↑Reactivity of Metals A, B, and C with dilute HCL is MOST REACTIVE Metal B → LESS REACTIVE Metal A → LEAST REACTIVE Metal C
The reactivity series of metals is a chart showing metals in order of decreasing reactivity. In general, the more reactive a metal is:
Rationale:
Reactions of metals and acids are very important in everyday life. The speed of a reaction is crucial, for example, in industrial processes where a product ought to be obtained as fast and as cheaply as possible for economic reasons. Do reactions take place at the same speed? This activity will help learners to answer this question.
Prerequisite/ Previous knowledge:
Acids, metals and reactions of dilute acids with metals and the products, writing and balancing chemical reaction.
Learning Materials:
Four Test tubes per group, dilute hydrochloric acid, rubber bands, balloons, metal powder labelled as A, B and C, Magnesium ribbon
Reference Materials:
New School Chemistry. By Ababio
Lesson Development:
| STAGE | TEACHER'S ACTIVITY | LEARNER'S ACTIVITY | LEARNING POINTS |
|---|---|---|---|
| INTRODUCTION full class session (5mins) |
The teacher asks the learners to write and balance the following reaction:
|
The learners attempted the teacher's questions:
|
Linking previous knowledge with the lesson |
| STEP 1 10 mins. Development |
The teacher writes on the whiteboard the topic and sub-topics.Activity 1Teacher shown learners the metal X and asked learners to identify its name. |
The learners identify its name. Magnesium ribbon |
Pre-requisite knowledge |
| The teacher reacted the Metal X with acid and ask learners to state the observations. | Learners observe the reaction of the metal with the acid and state the observations. (Hands and Minds-on activity) Learners identify the products formed. Learners suggest whether different metals react rapidly with acids. (Minds-on activity) |
Observation of the reaction
Predictions |
|
| STEP 2 10 mins. |
Activity 2Teacher explains the purpose of the activity as to investigate how fast metals A, B, and C react with dilute HCl.The teacher explains the procedure and precautions to be taken care of by the learners. Material/apparatus
PROCEDURE:
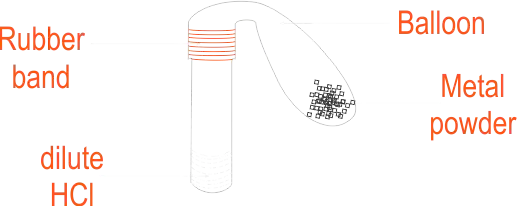 Reaction of metals with HCl
Reaction of metals with HCl
Precaution: Make sure no acid spills on your skin or clothes. |
Learners go through the instructions written in the paper to familiarise themselves with the activities and collect apparatus/chemicals and do the experiment. (Hands-on activity). Learners discuss and record the observations in their exercise books. (Minds-on activity) |
Cautions: Handling of the acid. Preparation of the experiments Meniscus of measuring cylinder |
| STEP 3 (5 mins) |
The teacher goes around to check on what learners are doing and assist where necessary. | Learners arrange the metal A, B and C in the order of the speed of reaction. Learners report on their observations and the order of the metals on the chalkboard. |
Observation and group discussions
|
| STEP 4 5 mins |
The teacher asks learners to identify Metals A, B, and C base on their observations. | Learners identify Metals A, B, and C: Metal A reaction with dilute acids was rapid, bubbles and hissing sounds are produced, the test tube becomes warm and a colourless solution was formed. Metal A is probably Magnesium. Metal B reaction with dilute acids was more rapid than metal A, bubbles are produced, the test tube was hot/warm than that of metal A and a colourless solution was formed. Metal B is probably Calcium. Metal C reaction with dilute acids was much less vigorous i.e very slow, with much smaller bubbles produced and pale green solutions formed when reaction went to completion, a yellow showery sparks and black solid were produced when the heat was applied. Metal C is probably Iron. |
Interpretation of the observation on the reactions |
| EVALUATION 3mins |
The teacher asks questions to the learners to evaluate the lesson.
|
|
Asking the learners questions to assess the achievement of the set objectives. |
| CONCLUSION 2mins |
The teacher guides the learners so that they come up with the concepts from the observations drawn. (Bridging the activities to the concept). | Metal B reacts faster than metal A and C in a given time. | Application: expansion of the concept |
|
|
|||
| ASSIGNMENT |
|
Learners answer other questions. | Improving their level of understanding on Reactivity Series of Metals using dilute HCl. |
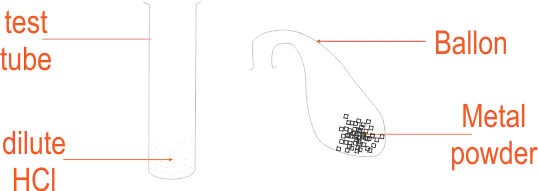 Reaction of metals with HCl Apparatus
Reaction of metals with HCl Apparatus