ASEI Lesson Plan on Biology
Lesson Note on Transport in Plants
Theme: Transport in Plants
Topic: Transport in Plant II
Sub Topic: Internal Structure of a Dicotyledonous Stem
Date: dd/mm/yyyy
Class: S.S.S 2
Duration: 35 Minutes
No of Learners: 30
Learning Objectives:
By the end of the lesson learners should be able to:Identify and draw the internal tissues of dicotyledonous stem under a light microscope.
Identify the plant tissue that is involved in the transportation of water and mineral salts in dicotyledonous stem using a light microscope.
- Vascular bundle
Compare the internal structure of a stem of monocotyledonous and dicotyledonous plants
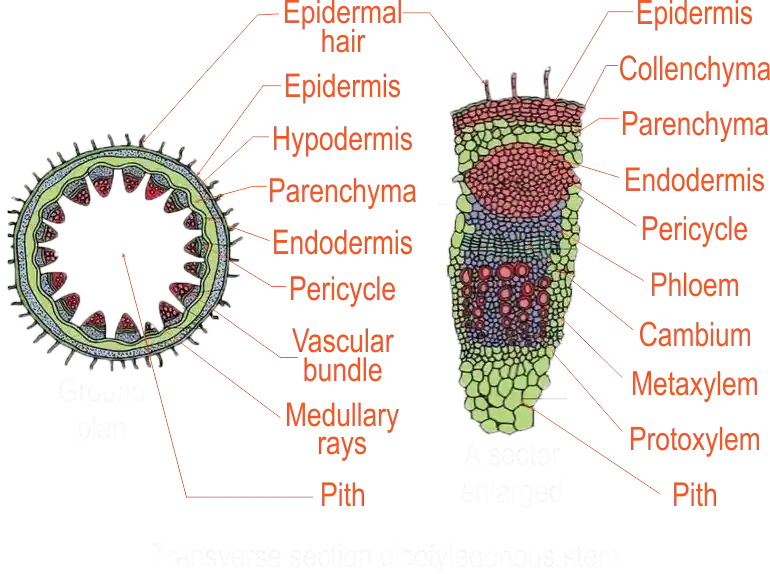 Dicotyledonous Stem
Dicotyledonous Stem
The part that transports water and mineral salts are;
Vascular bundles in dicotyledonous plants are arranged like a ring while those in monocotyledonous are scattered
Rationale:
The stem is a plant organ whose primary functions are to support the shoot, conduct water and mineral salts from the roots to the leaves and transfer manufactured food from the leaves to the other parts of the plants. Various tissues in the stem carry out these functions. Knowledge of this will make learners appreciate that the internal structures of monocotyledonous and dicotyledonous stems differ in a relation to the arrangement of their tissues.
Prerequisite/ Previous knowledge:
- Use of a light microscope
- Cell specialisation (Cells, tissues, organs)
- Preparation of temporary slides
- The internal structure of the monocotyledonous stem.
Learning Materials:
Light microscopes, scalpels, slides and cover slips, young dicotyledonous plant e.g. Bidens pilosa L. (Asteraceae) 'the black jack' and monocotyledonous plant, Petri dishes, water, eosin solution and a chart of the internal structures of stems, photomicrograph of a dicotyledonous stem, white tilesReference Materials:
Biology A New Approach For Senior Secondary Schools and Colleges By E. O. Egho,
Modern Biology for SSS By Kucy I. Aunwa et-al
Lesson Development:
| STAGE | TEACHER'S ACTIVITY | LEARNER'S ACTIVITY | LEARNING POINTS |
|---|---|---|---|
| INTRODUCTION full class session (5mins) |
The teacher provides Learners with 2 plants in flasks labelled A and B dipped in eosin dye, and ask learners:
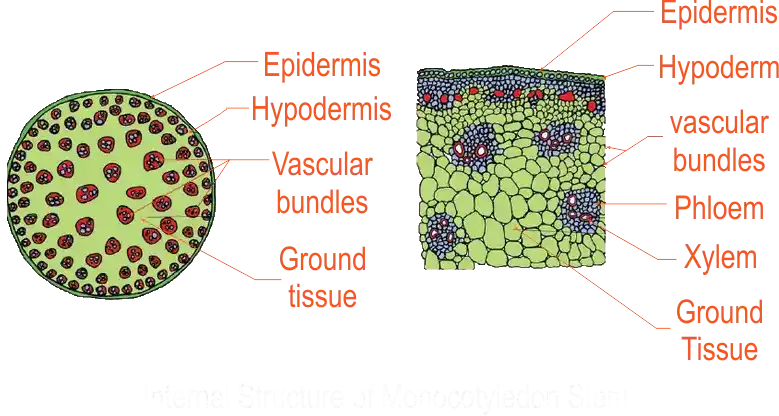 Monocotyledonous stem
Monocotyledonous stem
The teacher draws a table and list down the differences. |
Learners observe the two plants and identify the groups the plant belongs to.
The external differences between them are:
|
Observation and identification of plants |
The teacher asks learners the following questions;
|
Learners observe the two plants and notice what has happened to the red dye.
Learners look at the chart of a plan diagram of the internal structure of the monocotyledonous stem.
|
||
| Development (20 minutes) |
Activity 2 (Sectioning):The teacher provides material, apparatus and students worksheets. Teacher guide learners to perform the following activity;
Teachers supervise and guides students. |
The learners form working groups. The learners cut and mount transverse sections of the stem (Hand-on activity). Learners observe sections under the light microscope. |
CAUTION: about handling sharp cutting instruments (scalpel). Sectioning and manipulation of the microscope. For the vascular bundle of the stem to be seen learners must cut the transverse section. The specimen should be very thin to pass through light. |
| (Drawing and labelling) Learners draw a plan diagram of what they observe and they label the diagram as they discuss (Minds-on activity). Learners answer the following questions.
|
Recording observation by drawing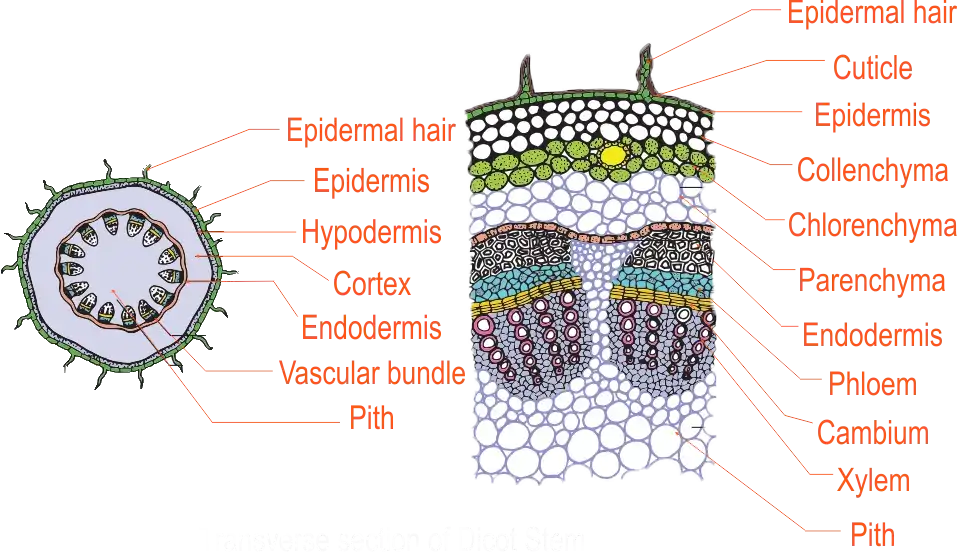 Decot System
Decot System
Reasoning and clarification
|
||
| EVALUATION (10 minutes) |
The teacher evaluates the lesson by posing questions;
|
|
Asking the learners questions to assess the achievement of the set objectives. |
| CONCLUSION 5mins |
The teacher consolidates the main points and corrects any misconceptions. | Learners consolidate the key areas of drawing and labelling plan diagrams. | The main points are no shading, continuous lines, use of sharp pencil and to draw what is observed. |
| ASSIGNMENT |
|
Learners answer other questions | Improving their level of understanding |