ASEI Lesson Plan on Biology
Lesson Note on Types of circulation
Theme: Circulatory System
Topic: Types of circulation
Sub Topic: Types of circulation
Date: dd/mm/yyyy
Class: S.S.S 2
Duration: 35 Minutes
No of Learners: 30
Learning Objectives:
By the end of the lesson learners should be able to:Define the circulatory system.
The circulatory system is a system of blood vessels with a pump and valves to ensure a one-way flow of blood.
List and explain the types of circulation.
There are two types of circulatory systems in animals:- closed circulatory system and
- open circulatory system.
- Open circulatory system: This is a circulatory system in which blood is in contact with body cells. In the open circulatory system, blood does not stay inside the vessels all the time because they are open-ended. Instead, the blood is pumped out of the vessels by a heart or pumping organ into a space within the body known as the haemocoel. This means that blood is in direct contact with the cells. The cells exchange materials directly with the blood. This blood eventually flows back into the heart due to the movement of the body muscles of the organism.
- Closed circulatory system: This is a circulatory system in which blood remains enclosed in a system of vessels. It circulates within these vessels due to the pumping action of the heart which is part of the system. In this way, waste substances from the tissues enter the blood vessels, while food substances from the blood vessels enter the tissues. The closed circulatory system is found in annelids and vertebrates like mammals. It has an advantage over the open circulatory system because the pressure of blood in it is high. This means that blood circulates faster and hence transports substances to and from the tissues faster than in the open systems.
Describe the single circulation of a fish and the double circulation of a mammal.
The single circulatory system: is a type of circulatory system in which blood passes through the heart once before it goes to the body. It is found in animals such as fish.List advantages of the double circulatory system over the single circulatory system and differences between the close circulatory system and open circulatory system.
- Blood flows into and from the body at relatively higher pressure therefore, blood can be pumped for a long distance.
- Oxygen and nutrients plus hormones are delivered to tissues at a higher speed than in the single circulatory system.
- Waste products are removed at a relatively higher speed from tissues to excretory organs.
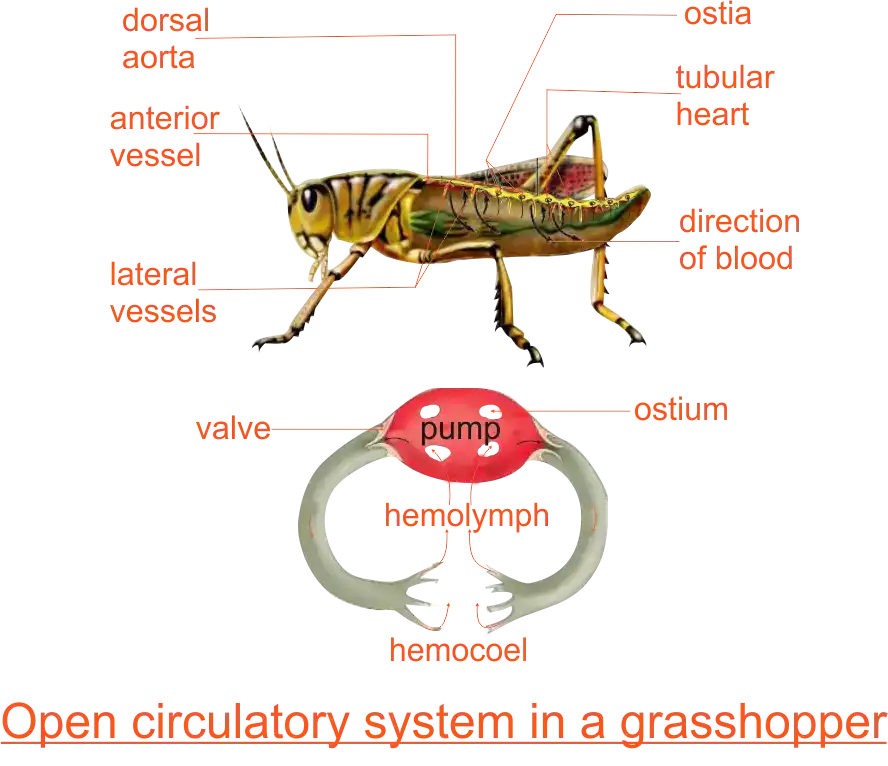 Open circulatory system
Open circulatory system
Insects’ circulatory systems consist of a long tubular heart along the backside (dorsal) of the organism. When the heart contracts, blood in it is forced out at its front end. The blood then flows into the haemocoel or body space where the exchange of materials with the tissues takes place. It then re-enters the heart through openings called Ostia. The open circulatory system works best in organisms with a small body cavity, for example, insects. It is not efficient for large organisms such as vertebrates.
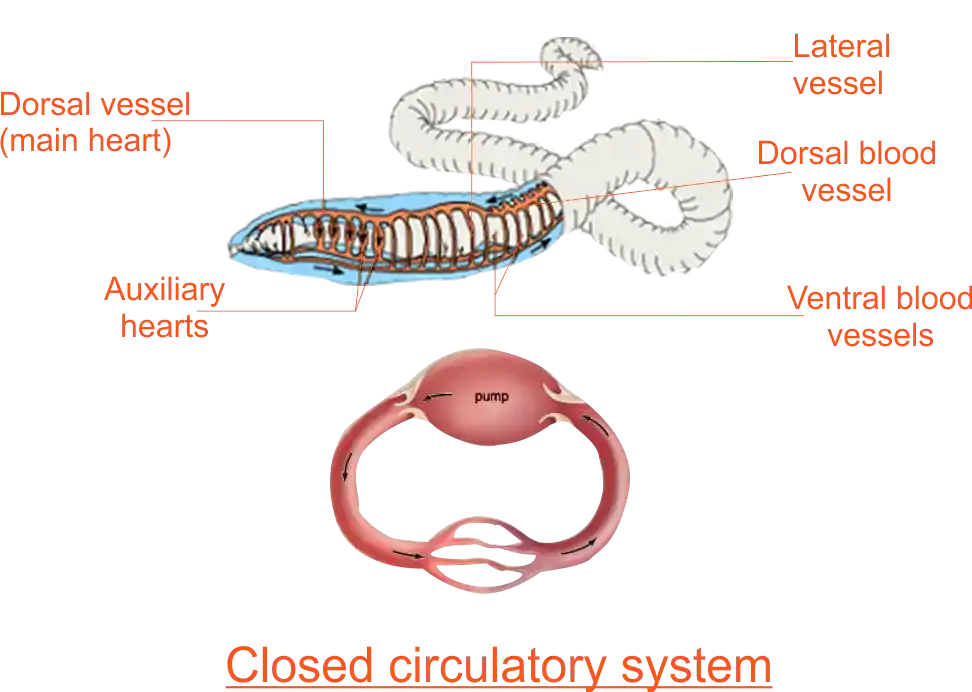 Close circulatory system
Close circulatory system
A closed circulatory system is a characteristic of vertebrates. However, there are significant differences in the structure of the heart and the circulation of blood among the different vertebrate groups due to adaptation and internal body structure (anatomy). There are two types of closed circulatory systems: single and closed circulatory system.
Fishes have a single circuit for blood flow and a two-chambered heart that has only a single atrium and a single ventricle. The atrium collects blood that has returned from the body, while the ventricle pumps the blood to the gills where gaseous exchange occurs and the blood is re-oxygenated; this is called gill circulation. The blood then continues through the rest of the body before arriving back at the atrium; this is called systemic circulation.
This unidirectional flow of blood produces a gradient of oxygenated to deoxygenated blood around the fish's systemic circuit. The result is a limit in the amount of oxygen that can reach some of the organs and tissues of the body, reducing the overall metabolic capacity of fish.
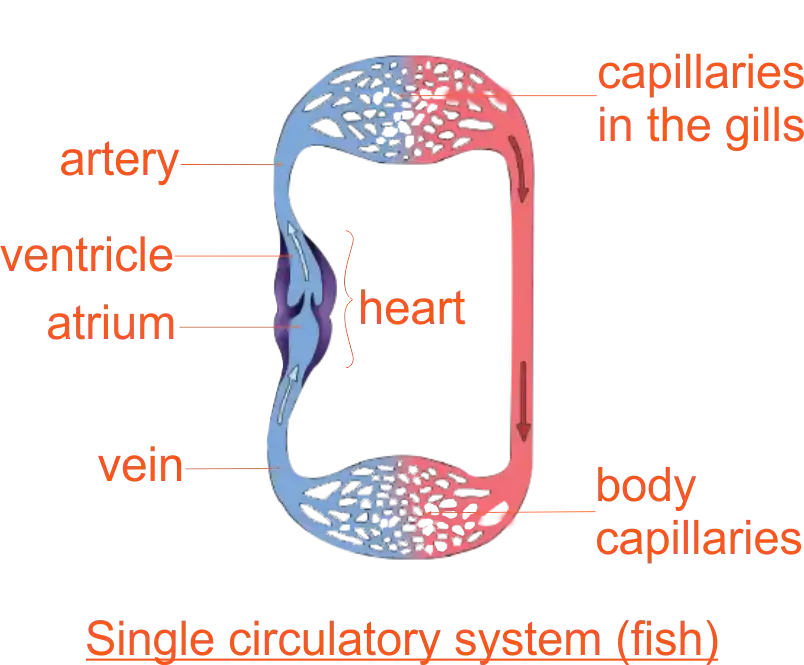 Single circulatory System
Single circulatory System
The double circulatory system is the type of circulatory system in which blood passes through the heart twice before completing a full circuit. It is found in the body of mammals and birds.
In this type of circulation, the pulmonary circulation is separate from systemic circulation. Pulmonary circulation carries deoxygenated blood away from the heart to the lungs and returns oxygenated blood to the heart. Systemic circulation carries oxygenated blood away from the heart to the body, and returns deoxygenated blood back to the heart.
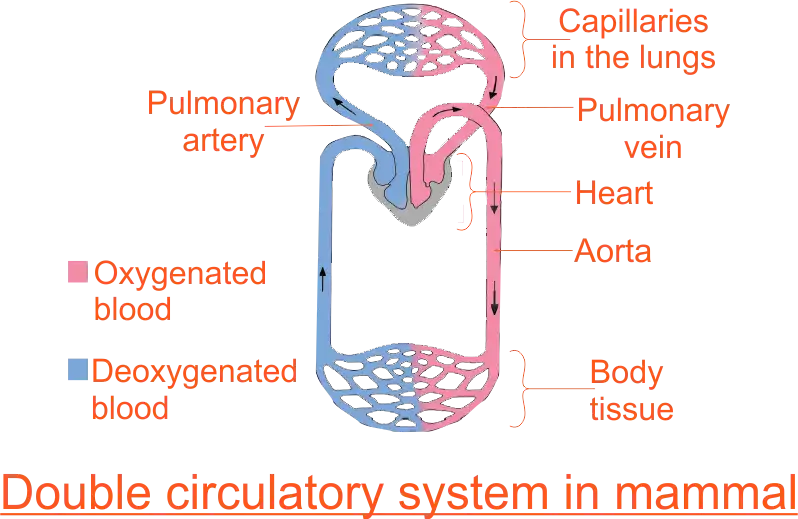 Double Circulatory System
Double Circulatory System
| Closed circulatory system | Open circulatory system |
|---|---|
| Present in annelids and vertebrates | Present in invertabrates |
| Blood does not bathe the cells | Blood directly bathes the cells |
| There is a muscular heart | There is no muscular heart but nodes as the simple heart |
| High blood pressure | Lower pressure |
| Blood contains haemoglobin | There is no haemoglobin |
| They have blood | they have no blood but a carring liquid |
| Examples, earthworms, fish, frogs and human beings. | Examples, insects and orchids e.g, spiders, scorpions and harvestrons. |
Rationale:
All animals except small animals need a circulatory system to transport substances from one cell to a cell because the cell has to be provided with some of the nutrients, oxygen and to remove some waste products from it such as carbon and nitrogenous waste products. The heart acts as the pump for the blood. Even when the body is at rest, this incredible organ pumps more than 6,000-7,500 litres of blood daily. The heart works closely with blood vessels which convey blood to the various body organs. If a cell is not provided with nutrients and oxygen (blood), the cell will not survive.Prerequisite/ Previous knowledge:
- The function of the heart
- Cell specialisation (Cells, tissues, organs, system)
Learning Materials:
Demo of hot water supply system in a house, Video on circulation of blood, diagrams of grasshopper, earthworm and human circulatory system.Reference Materials:
Biology A New Approach For Senior Secondary Schools and Colleges By E. O. Egho,Modern Biology for SSS By Kucy I. Aunwa et-al
Internet.
Lesson Development:
| STAGE | TEACHER'S ACTIVITY | LEARNER'S ACTIVITY | LEARNING POINTS | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| INTRODUCTION full class session (5mins) |
The teacher asks learners to place their right palm firmly on the left side of your chest and ask learners:
|
Learners response to teacher's question.
|
Confirming previous knowledge. | ||||||||||||||||
| INTRODUCTORY ACTIVITY full class session (5mins) |
The teacher gives learners two diagrams to study; a hot water supply system in a typical house and circulation of blood in the body. The teacher explains to learners that in the hot water supply system the blue pipes in the diagram convey cold water whereas the red pipes convey hot water. The teacher asks learners, in the blood circulatory system diagram,
|
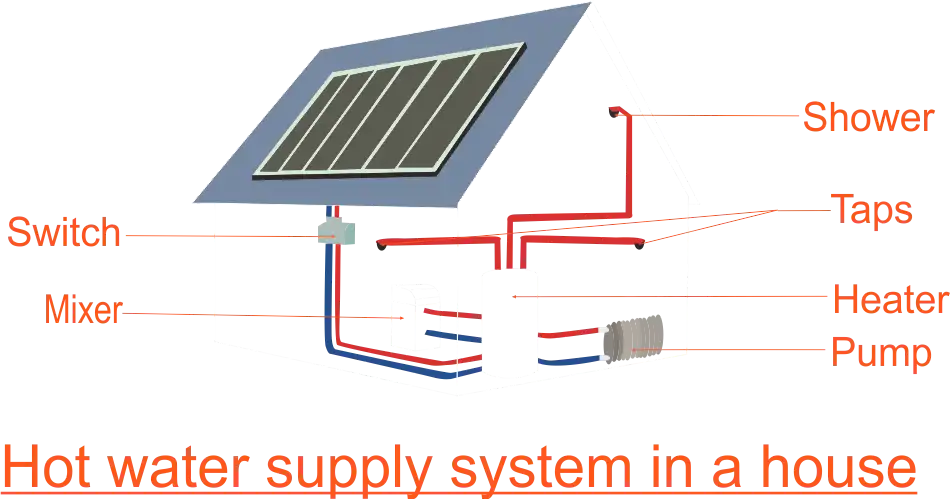 Hot water supply System
Hot water supply System
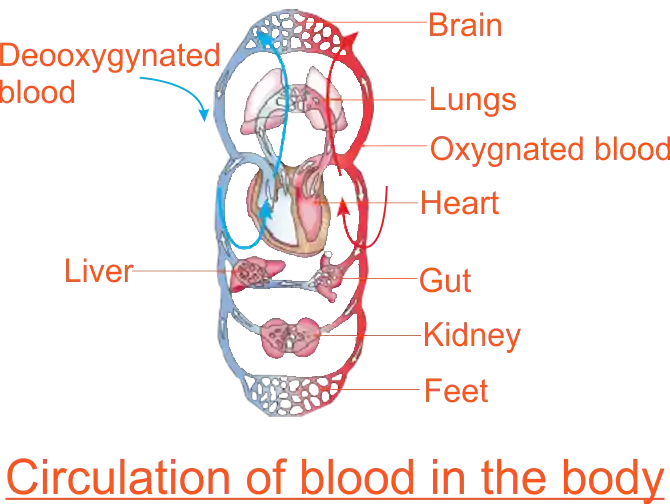 Blood Circulatory System
Blood Circulatory System
Learners observe the two diagrams and deduce the circulatory system of human beings. The human circulatory system is responsible for pumping blood throughout the body. The heart acts as the pump for the blood. |
Developing the idea of the circulatory system from the two diagrams. | ||||||||||||||||
| Development 2 (10 minutes) |
Activity 2 :The teacher explain to learners that circulation can either be a closed circulatory system or an open circulatory system. The teacher provides learners two diagrams;
|
 Open Circulatory System
Open Circulatory System
 Close Circulatory System
Close Circulatory System
The learners form working groups. Learners expected response.
| Open and close circulatory system | ||||||||||||||||
| Development 3 (5 minutes) |
The teacher gives learners two diagrams to study in a group and ask learners what they observe about the type of circulation in each of the diagrams and what possible name or type of close circulation could it be? The teacher guide learners to list the advantages of a double circulatory system over the single circulatory system |
 Single Circulatory System
Single Circulatory System
 Double Circulatory System
Double Circulatory System
Learners expected response.
The Learners list the advantages of a double circulatory system over a single circulatory system. |
Single and double circulatory system. | ||||||||||||||||
| EVALUATION (5 minutes) |
The teacher evaluates the lesson by posing questions;
|
|
Asking the learners questions to assess the achievement of the set objectives. | ||||||||||||||||
| CONCLUSION 5 mins |
The teacher consolidates the main points and corrects any misconceptions. | Learners consolidate the key areas of drawing and labelling plan diagrams. | The main points are no shading, continuous lines, use of sharp pencil and to draw what is observed. | ||||||||||||||||
| ASSIGNMENT |
|
Learners answer other questions | Improving their level of understanding | ||||||||||||||||